Seven Practical Precautions in Drawing Die Design for Stable and High-Quality Stamping
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Dec 29,2025
Why Drawing Die Design Is Critical in Stamping Production
Drawing dies account for a significant proportion of the stamping die industry.
From motor housings and metal cups to structural shells, most stamped products involve stretching processes.
Unlike simple cutting dies, drawing die design cannot rely solely on theoretical calculations.
Many variables such as material properties, drawing direction, blank holder force, and forming limits directly affect the final result.
Especially for non-rotational or irregular parts, drawing design becomes more complex and experience-driven.
At saivs, years of practical tooling experience show that successful drawing die design is achieved through engineering judgment, controlled trials, and optimized process planning.
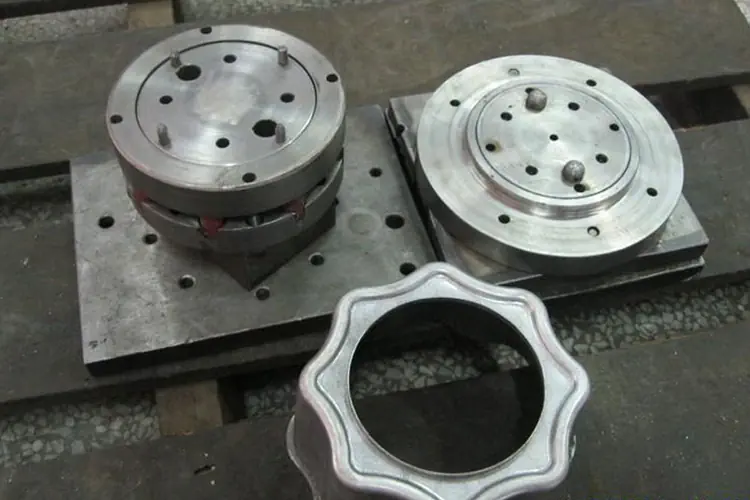

Material Selection: The Foundation of Successful Drawing
Choosing the Right Stretching Material
When repeated mold trials fail to meet product requirements, changing the material is often the most effective solution.
Material selection determines more than half of the drawing success.
Common cold-rolled steel sheets used for deep drawing include 08Al, 08, 08F, 10, 15, and 20 steel.
Among them, 08 steel is widely used and available as rimmed steel and killed steel.
Rimmed steel offers lower cost and good surface quality, but it suffers from segregation and strain aging.
It is not suitable for parts requiring high appearance quality or deep drawing performance.
Killed steel, such as 08Al aluminum-killed steel, provides more uniform properties and better drawability.
Imported materials like Japanese SPCC-SD deep drawing steel offer even higher tensile performance.
Mold Surface Finish and Its Impact on Drawing Quality
The surface finish of the die directly affects friction and material flow.
Insufficient polishing of the die cavity or blank holder can cause drawing scratches.
This issue is especially serious when drawing stainless steel or aluminum sheets.
In severe cases, surface damage may lead to tensile cracking and scrap parts.
SAIVS recommends fine grinding and polishing of all drawing contact surfaces to reduce friction and improve material flow.
Determining the Correct Blank Size
Wrinkles Are Better Than Cracks
In drawing design, the guiding principle is “more wrinkles, fewer cracks”.
Wrinkles can often be corrected in later processes, while cracks usually mean part failure.
For simple rotational parts, blank size can be calculated by equal-area principles.
However, most deep-drawn parts involve complex shapes, thinning, or multi-stage forming.
Although 3D unfolding software exists, its accuracy is still limited in practical production.
Blank Trial Strategy
In real production, SAIVS engineers recommend reserving flexibility during Mold design.
The blanking die should not be finalized too early.
Initial blanks can be cut by wire cutting or milling.
After multiple drawing trials, the final blank size is confirmed before finishing the blanking die.
Stretching Coefficient: A Key Process Parameter
The stretching coefficient m is a core parameter used to determine drawing sequence and number of stages.
It is influenced by material properties, thickness ratio, drawing method, lubrication, die fillet radius, and forming speed.
Most engineers determine the stretching coefficient using stamping manuals and empirical tables.
However, parameters such as material thickness and drawing method are difficult to change after mold manufacturing.
Therefore, careful review and cross-checking during design are essential.
Processing Oil Selection and Lubrication Method
Lubrication plays a decisive role in preventing cracks and reducing friction.
If the drawn part temperature is too high to touch after forming, lubrication is insufficient.
In cases of tensile cracking, lubricating oil should be applied to the concave die only.
The convex punch should remain clean.
For difficult materials, a plastic film with thickness of 0.013–0.018 mm can be placed between the sheet and concave die.
Intermediate Annealing: When and Why to Use It
During deep drawing, cold work hardening reduces material plasticity.
This increases deformation resistance and may lead to cracking.
Intermediate annealing can restore plasticity through recrystallization.
However, it also increases production cost.
Annealing Considerations
Oxidation and decarburization must be controlled during annealing.
Oxide scale reduces effective thickness and accelerates mold wear.
When advanced equipment is unavailable, practical methods include protective packing or pickling after annealing.
Bright annealing using nitrogen furnaces provides the best surface quality when conditions allow.
Additional Practical Design Recommendations
Clear Dimension Definition
Product drawings should clearly specify whether internal or external dimensions are critical.
Inner and outer dimensions should not be controlled simultaneously.
Crack Analysis
Irregular cracks often indicate material defects.
Clean and straight cracks usually result from process or mold design issues.
Improving Wear Resistance
Punches, dies, and blank holders should be quenched, hard-chrome plated, or surface-treated.
For extreme conditions, tungsten carbide inserts may be used.
Why Choose SAIVS for Drawing Die Solutions
SAIVS provides professional stamping die solutions backed by real production experience.
From material selection to lubrication strategy and mold surface treatment, every detail is optimized for stability.
Our drawing dies are designed to reduce trial costs, improve forming success rates, and ensure consistent product quality.
Partnering with SAIVS means reliable tooling, practical engineering support, and long-term manufacturing value.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Causes and solutions of deformation of aluminum alloy die castings
Aluminum alloy die casting is widely used in various industries due to its excellent characteristics such as light weight, high strength, and good corrosion res...
-
6 Effective Strategies to Stop Rust in its Tracks
Learn how to prevent rust with smart choices & clever tricks. From steel secrets to coatings & care, keep your projects strong & beautiful. Start ru...
-

Aluminium Casting Vs. Steel Casting: Which Alloy Is Right For Your Product
Introducing Green Sand CastingCasting products are used in a variety of industries, making casting an important manufacturing process. Many of these products ar...
-

From Iron Alloys to Aluminum Alloys: Understanding the World of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals
Delve into the world of metals with this comprehensive guide to ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Explore their properties, applications, and key differences.
-

Key Factors Affecting the Quality and Accuracy of Investment Casting
Investment casting is a versatile and widely used casting process that can produce highly precise and complex parts with excellent surface finish and dimensio...
-

Maximizing Thread Cutting Efficiency with Indexable CNC Turning Tools
Maximizing Thread Cutting Efficiency with Indexable Thread Turning ToolsIn the world of CNC machining, selecting the right tools and cutting technology is

