Practical Solutions for Internal Defects in Aluminum Alloy Die Castings — SAIVS Technical Guide
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Oct 21,2025
Practical Solutions for Internal Defects in aluminum alloy Die Castings
This technical guide explains the common internal defects found in aluminum alloy Die Castings and provides practical, production-ready solutions.
The content is written to help purchasing engineers, quality managers, and procurement teams quickly identify root causes and select saivs parts or services that reduce scrap and improve yield.
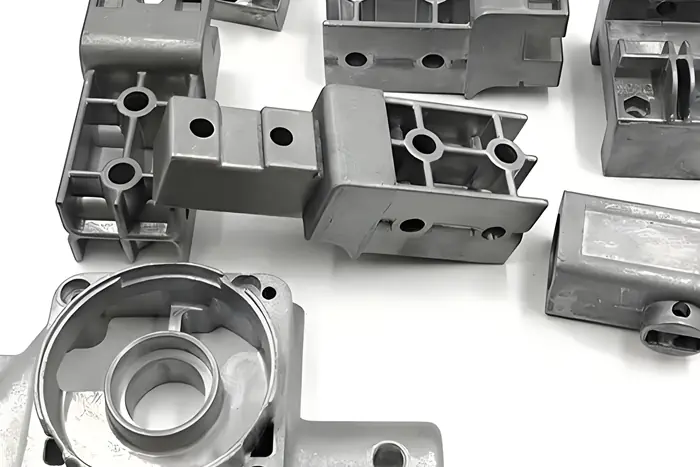

1. Overview of Key Internal Defects
aluminum die castings commonly exhibit internal defects such as gas porosity, shrinkage and porosity, inclusions, brittleness, leakage, and hard spots.
Each defect has distinct morphology and detection methods, including visual inspection, pressure/leak tests, metallography, and non-destructive testing (NDT).
Gas Porosity (Blowholes)
Characteristics: round, smooth cavities visible after sectioning or by X-ray inspection.
Typical causes: trapped air created by high flow velocity, poor venting, excessive dissolved gas from contaminated or overheated melt, and heavy use of gas-bearing coatings.
Shrinkage and Porosity
Characteristics: irregular, dark cavities that form where metal feeding is inadequate during solidification.
Typical causes: insufficient pressure compensation, low boost pressure, thin gates or insufficient metal charge, and localized hot spots in part geometry.
Inclusions and Hard Spots
Characteristics: metallic or non-metallic particles embedded in the casting that increase tool wear and reduce surface quality.
Typical causes: dirty charge material, entrained slag, refractory or coating debris, graphite spalling, and improper pouring technique.
2. Inspection and Early Detection
Effective defect control begins with robust inspection.
Implement a layered inspection plan: visual checks at the machining stage, pressure/leak testing for fluid components, and X-ray or ultrasonic NDT for critical structural parts.
Metallographic analysis should be used periodically to verify grain size and inclusion content.
3. Practical Process Controls and Remedies
Below are targeted remedies linked to specific defect types that can be implemented quickly on the shop floor or via minor tooling and process upgrades.
Remedies for Gas Porosity
Use clean furnace charge and remove contaminants before melting.
Maintain optimized melt temperatures and apply degassing and flux/refinement procedures to remove dissolved hydrogen.
Balance injection parameters: reduce excessive fill velocity and set correct high-speed switch points to avoid vortex formation.
Design and maintain effective venting: add exhaust grooves and adequate overflow capacity to the die.
Remedies for Shrinkage and Porosity
Lower pouring temperature within the recommended range to reduce shrinkage volume.
Increase injection and boost pressures to improve feeding and metal density.
Enlarge or modify inner gates to improve pressure transmission and prevent premature solidification.
Reassess part design: eliminate abrupt cross-section changes and reduce hot spots by evening wall thickness or adding chills/heat sinks where necessary.
Remedies for Inclusions and Hard Spots
Source high-quality alloy ingots and limit the proportion of reclaimed material.
Refine and clean the melt, skim slag before pouring, and avoid scooping oxide layers with the pouring ladle.
Use non-reactive crucible linings and ensure coating materials do not shed into the melt.
Schedule regular maintenance to remove residue from crucibles and ladles.
4. Metallurgical and Equipment Adjustments
Control alloy chemistry carefully to avoid exceeding impurity limits for elements such as Fe, Zn, Pb and Sn.
Adjust thermal profiles: reduce holding times to prevent grain coarsening and avoid excessive cooling that causes overly fine grains.
Increase mold temperature where grain coarseness is an issue and optimize die heating/cooling circuits for uniform solidification.
5. Mold and Process Prioritization — A Practical Sequence
When defects occur, use a tiered approach to troubleshooting that emphasizes low-cost, high-impact actions first.
1) Clean parting surfaces, cavities, and ejector pins to remove debris and trapped contaminants.
2) Improve die coatings and spray technique, and verify clamping force.
3) Adjust process parameters such as injection speed, boost pressure, and shot profile.
4) If defects persist, repair worn mold components, stiffen the die where flashing or deformation appears, and consider gating/exhaust redesigns.
6. Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Recommendations
Incorporate DFM principles early: maintain uniform section thickness, use gradual transitions for area changes, and plan gating and vents to support directional solidification.
Add local feeders, overflow wells, and exhaust traps in high-risk regions identified by simulation or early trials.
Run solidification and flow simulation during design to predict potential shrink zones and trapped-air areas before tooling is produced.
7. How SAIVS Helps Reduce Risk and Cost
SAIVS supplies precision tooling components, high-quality alloy materials, and process consultation to reduce internal defects and improve yield.
By partnering with SAIVS, procurement teams gain access to validated die modifications, controlled alloy sourcing, and on-site troubleshooting that translate to fewer rejects and lower total cost of ownership.
Conclusion — Action Plan for Procurement and Quality Teams
Start with a simple triage: clean tooling, check melt quality, and adjust key shot parameters.
If defects remain, escalate to metallurgical analysis and mold redesign with targeted additions like inner gates, overflows, and vents.
Work with SAIVS for material traceability, process audits, and engineered tooling upgrades to achieve measurable yield gains.
Contact SAIVS to request a defect analysis or a quotation for replacement tooling and quality alloys.
Call to Action: Contact SAIVS engineering for a production audit and quotation to reduce Casting Defects and improve delivery confidence.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Influence of Metal Forging Process on Part Quality
Through the analysis of forging defects, this paper puts forward suggestions for optimising the forging process, aiming to improve the quality of forgings.
-

Repairing Defects in Investment Castings
From the defect causes to repair methods, a comprehensive analysis of investment casting defects repair knowledge, help you to understand the casting process.
-

Enhancing CNC Machining with Wavelet Analysis for Accurate Overcut Detection
In the realm of CNC machining, precision and efficiency are paramount, especially in complex applications like mold manufacturing.However, challenges such
-

How Casting Patterns Shape Metal Manufacturing
Uncover the steps in manufacturing sand castings and the importance of optimizing the casting process.
-

What are the requirements for precision die casting?
Precision Die Casting: A Superior Metal Forming TechnologyPrecision die casting is a cutting-edge manufacturing process that allows for the creation of int
-
Investment Casting: Unveiling the Magic of Wax Patterns
This guide delves into the various types of investment casting waxes, their unique properties, and how they contribute to the success of this versatile techniqu...

