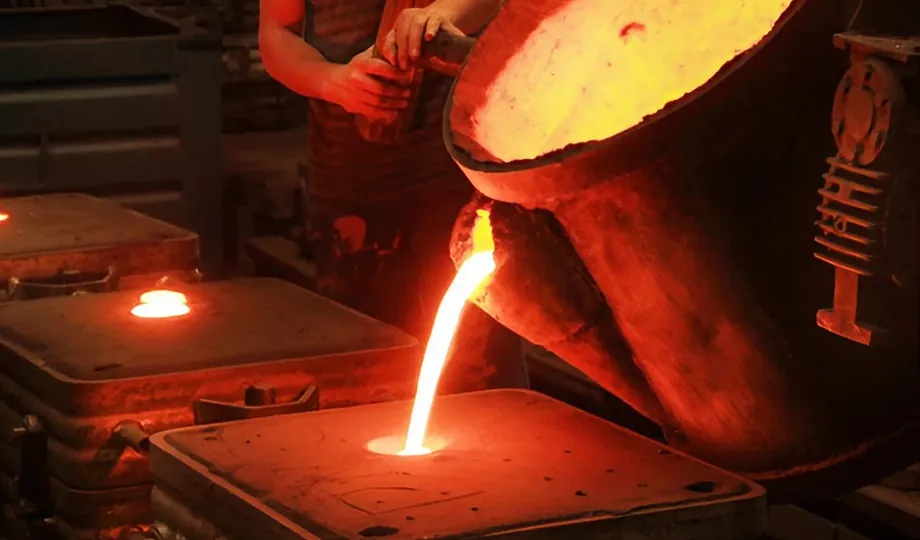
The 6-Step Process of Sand Casting: A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Metal Castings
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Feb 22,2024
I. Sand Casting and Its Working Principle
Sand casting is a metal casting process that uses sand as the primary molding material.
It is one of the oldest and most widely used casting methods due to its versatility, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
The working principle of sand casting is relatively simple. A pattern, which is a replica of the desired casting, is created in the sand.
Molten metal is then poured into the mold cavity, where it solidifies and takes the shape of the pattern.
Once the metal has cooled and solidified, the casting is removed from the mold and cleaned.
II. Key Components in Sand Casting
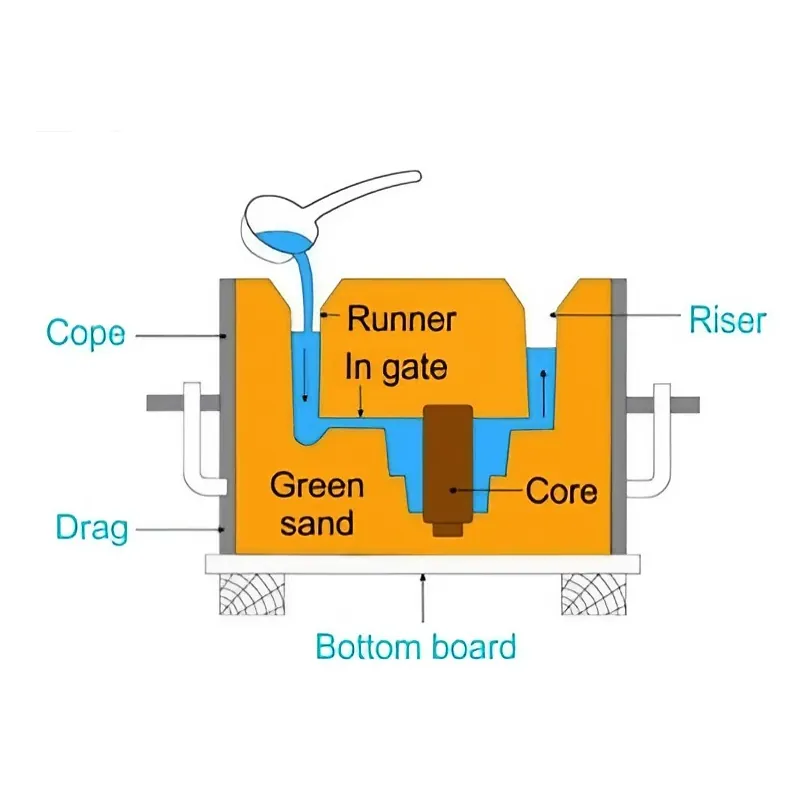
Pattern: A replica of the final part used to create the mold cavity in the sand.
Molding Box: A container that holds the sand and pattern during molding.
Gating System: A network of channels that guides the molten metal from the pouring spoon into the mold cavity.
Cores: Inserts used to create internal cavities or features in the casting.
Risers: Reservoirs of molten metal that compensate for solidification shrinkage and ensure sound casting.
III. Sand Casting Step-By-Step Process
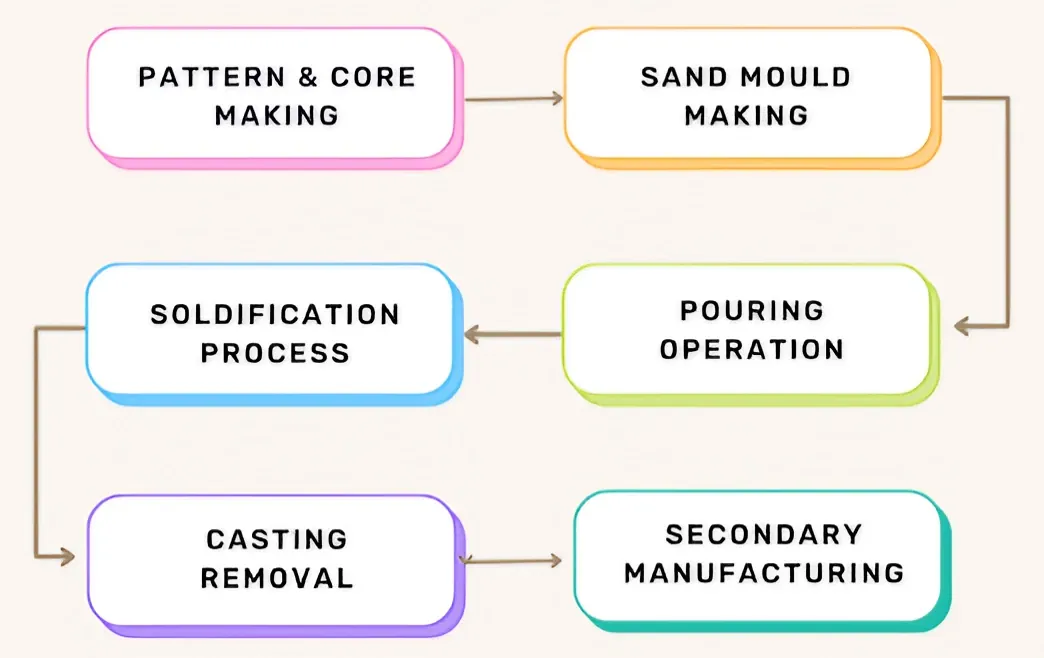
Step1:Pattern & Core Making
Wooden, plastic, or metal patterns create the mold cavity.
Sand cores form internal features like holes.
Care in Pattern Making:
Consider pattern material, geometry, withdrawal method, distortion, and shrinkage.
Apply pattern-making allowances like rapping, shrinkage, distortion, draft, and machining.
Color-code patterns for easy visualization during the molding process.
Step2:Mold Preparation
Purpose: Creating a mold using various types of sand, additives, binders, and water.
Types: Hand molding and machine molding.
Sand Types: Facing sand, system sand, green sand, dry sand, parting sand, loam sand, core sand, and backing sand.
Mold Structure: Cope, drag, flask, gating system (pouring basin, sprue, runner, riser).
Methods: Hand molding is a manual process, while machine molding involves the automated creation of green sand molds.
Step3:Melting & Pouring
Metal is melted in a furnace (electric arc, induction, etc.).
Molten metal is carefully poured into the mold.
Step4:Solidification & Cooling
Metal solidifies, potentially with a riser to feed material.
Controlled cooling ensures proper structure.
Step5:Shakeout & Cleaning
Mold is broken, casting is removed, and the gating system is cut off.
Sandblasting or other methods clean the casting.
Step6:Inspection & Finishing
Methods: Visual inspection, magnetic testing, NDT, ultrasonic testing, eddy current inspection, geometrical dimensions,
pressure testing, radiographic testing, metallurgical control, and inspection.
Secondary Manufacturing Process:
Finishing Operations: Grinding, turning, milling, lapping, honing, welding, repairing, CNC machining.
Heat Treatment: Annealing, normalizing, and hardening.
Final Touch: Powder coating, polishing, and painting for the final product.
This comprehensive process involves careful consideration of materials, equipment, and techniques at each stage to produce high-quality sand castings.
IV. Comparison with Other Casting Methods
Sand Casting vs. Investment Casting
Investment Casting: Uses a ceramic mold created from a wax pattern, offering higher precision and surface finish but at a higher cost and longer lead time.
Sand Casting: Utilizes a sand mold, making it less precise but more cost-effective and suitable for larger castings.
Sand Casting vs. Die Casting
Die Casting: Uses a permanent metal mold, enabling high production rates and precise castings but limited to simpler shapes and higher tooling costs.
Sand Casting: Offers greater flexibility in part design and shape complexity but with lower production rates and dimensional accuracy.
Advantages&Disadvantages of sand casting
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Versatility | Dimensional accuracy |
| Flexibility | Surface finish |
| Cost-effectiveness | Molding materials |
| Rapid prototyping | Environmental impact |
V.Sand Casting FAQ
1. Which sand is used for sand casting?
Silica sand, the most common and affordable option, is less heat-resistant; green sand, containing clay and moisture, provides good strength and reusability;
and no-bake sand, chemically bonded and not requiring baking, may be more expensive.
2. When was sand casting invented?
Sand casting is one of the oldest metalworking techniques, dating back to at least 1600 BC in China, possibly even earlier.
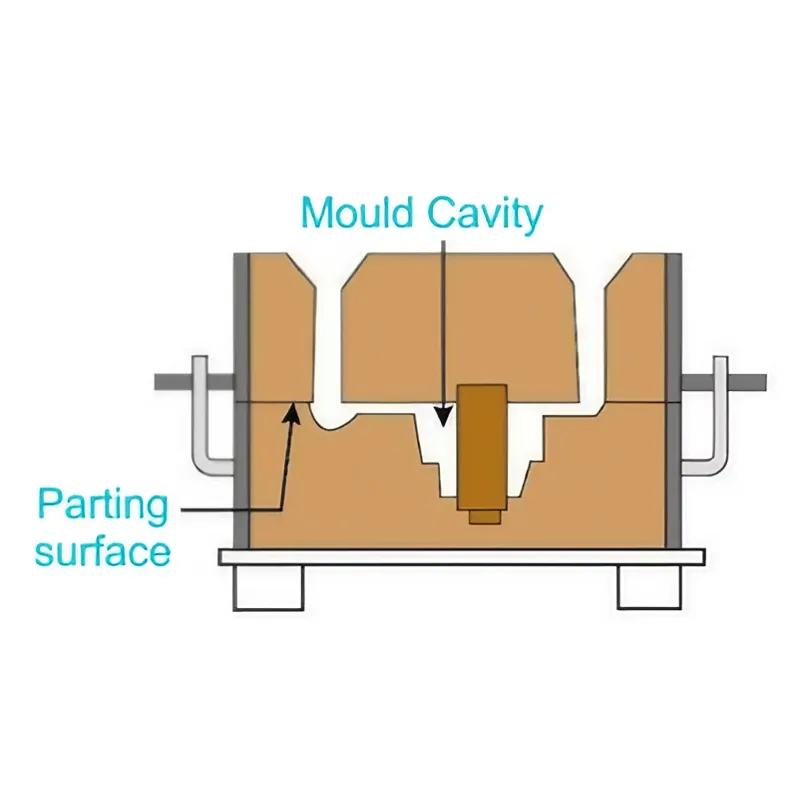
3. How to decide the parting line in sand casting?
Design the mold with minimized complexity and assembly challenges, ensuring easy removal of pattern and core inserts, while also accommodating features
such as cores and gating systems.
4. What are the applications and casting products made from the sand casting process?
Automotive: Engine blocks, cylinder heads, wheels, brake calipers.
Construction: Pipes, valves, fittings, structural components.
Machine tools: Gears, housings, brackets, levers.
Consumer goods: Cooking utensils, furniture hardware, decorative items.
5. Why is sand casting preferred and widely used?
The casting process boasts versatility by enabling the casting of diverse metals and complex shapes, ensuring cost-effectiveness for small-to-medium production volumes, and offering flexibility through relatively easy pattern modifications, all while utilizing widely available materials such as sand and basic equipment.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

What are the requirements for precision die casting?
Precision Die Casting: A Superior Metal Forming TechnologyPrecision die casting is a cutting-edge manufacturing process that allows for the creation of int
-

Optimizing Tool Materials for Efficient Cast Iron Machining
In the competitive landscape of the machinery industry, improving processing technology and increasing efficiency are crucial for reducing overall costs. O
-

An overview of Gravity Die Casting
An overview of Gravity Die CastingGravity die pourGravity die casting is used to manufacture casting parts from non-ferrous materials such as aluminium or low-t...
-

Influence of Metal Forging Process on Part Quality
Through the analysis of forging defects, this paper puts forward suggestions for optimising the forging process, aiming to improve the quality of forgings.
-

Advantages and precautions of aluminum alloy gravity casting?
The thickness of the outer wall of aluminum alloy castings in the process of gravity casting is called wall thickness, which is an important factor in the proce...
-

Demystifying the World of Aluminum and Steel Castings
IntroductionAluminum and steel are two of the most popular materials used in casting. Both materials have their unique advantages and disadvantages, making them...


