Die Casting vs Stamping: A Practical Guide to Choosing the Best Metal Forming Method for Your Parts
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Sep 22,2025
Die Casting vs Stamping — Practical Differences Every Buyer Should Know
Die casting and stamping are both mass-production metal forming methods but they serve different engineering and commercial needs.
Choosing the right process early saves tooling cost, shortens time-to-market, and improves part performance.
Fundamental process comparison
Stamping deforms sheet metal using a die and punch; it removes or reshapes material from a solid sheet in a high-speed press operation.
Die casting injects molten metal into a steel mold under pressure and then solidifies the metal to form near-net-shape parts.
Stamping excels for thin, high-volume sheet parts such as brackets, panels and housings.
Die casting is ideal for complex 3D geometries, enclosed cavities, and parts that require good surface finish and dimensional stability.
Materials and mechanical properties
Stamping typically works with stainless steel, mild steel, copper, and aluminum sheets.
Die casting commonly uses zinc, aluminum, magnesium and their alloys for tight tolerances and improved mechanical properties through pressure-assisted solidification.
Die-cast parts often achieve better as-cast surface finish (often Ra1.6 or better) and superior dimensional consistency.
Stamped parts can be lighter and are often preferred when sheet thickness and springback control are primary concerns.
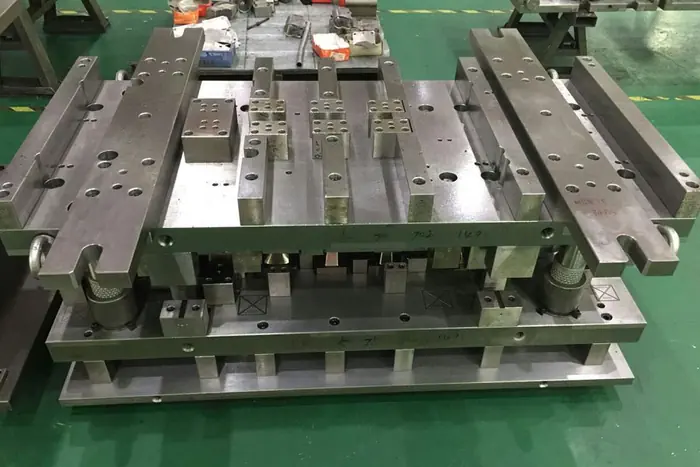
Tooling and mold differences
Stamping dies are usually simpler and lower-cost for small to medium production volumes, but progressive or compound dies add complexity and cost for multi-station forming.
Hot stamping requires dedicated die designs and cooling strategies to control springback and part strength.
Die-casting molds (dies) require hardened steel, precise cooling channels and often insert tooling to maintain cavity accuracy under thermal cycling.
Both processes need careful tool design: stamping for progressive operations and die casting for gate placement, vents and ejection systems.
Hot stamping die design types
There are four common hot-stamping die manufacturing approaches: drilling-type, layered-type, shower-type and casting-type.
Drilling-type dies are easy to machine and replace but cooling uniformity can be limited.
Layered-type dies offer better conformity and heat exchange but need high-precision machining and more complex sealing.
Shower-type dies spray high-pressure coolant for excellent quenching but risk water residues that shorten life if not managed.
Casting-type dies allow flexible cooling pipe layouts and strong heat transfer but require careful metallurgical joining and are harder to repair.
Production economics and quality trade-offs
For extremely high volumes of thin-sheet components, stamping gives the best cost-per-part once tooling is amortized.
For medium-to-high volumes of complex cast parts, die casting can reduce machining and finishing steps and improve part consistency.
Consider secondary operations: stamped parts may need welding, trimming or plating while die-cast parts frequently need machining of critical features and surface finishing.
Supplier capabilities and QC systems are critical — choose a partner that documents tolerances, SPC and material certifications.
How to choose: a short decision checklist
Geometry: Use stamping for flat or bent sheet features and die casting for intricate 3D shapes and internal cavities.
Volume: For very high sheet-part volumes choose stamping; for complex cast shapes at scale choose die casting.
Tolerance & finish: Die casting often wins for as-cast finish and dimensional accuracy; stamping wins for thin wall consistency and lower weight.
Material: Match alloy selection to requirements — aluminum/zinc for die casting; steel/aluminum sheet for stamping.
Why choose saivs for procurement and custom production
SAIVS delivers both precision die-casting parts and high-quality stamping services under one roof to simplify sourcing and reduce supplier management.
We provide engineering for manufacturability, prototype feedback, sample approval and full production-scale Quality Controls to help you launch faster and cheaper.
For buyers needing customization, SAIVS offers material traceability, tooling lifecycle planning and competitive quoting that reflects realistic lead times and batch pricing.
Contact SAIVS to request a quote, discuss prototype runs, or evaluate cost comparisons between die casting and stamping for your part.
Summary and next steps
Key takeaway: Match process to part function — stamping for sheet-based designs and die casting for complex cast geometries and tight finishes.
If you need an actionable cost-quality assessment for a specific part, SAIVS can provide DFM feedback and a turnkey quote to help you decide.
Ready to convert drawings into production? Submit your CAD and target volumes to SAIVS and get a Customized feasibility and quotation package.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Integrating CT and CAE Technologies in Die Casting for Smarter Quality Control
Digital Transformation of Die Casting: Intelligent Manufacturing and Real-Time Quality ControlDie casting has evolved into a highly digitalized and automat
-

Aluminium Casting Vs. Steel Casting: Which Alloy Is Right For Your Product
Introducing Green Sand CastingCasting products are used in a variety of industries, making casting an important manufacturing process. Many of these products ar...
-

Die Casting Temperature Control: Improve Casting Quality and Production Efficiency
Die casting mold temperature affects casting quality and productivity. Learn how to control temperature for optimal casting.
-

High-Quality Gray Iron Casting Gearbox Housing by SAIVS
Discover the exceptional range of Gray Iron Casting Gearbox Housing, crafted by the reputable SAIVS factory in China. Unbeatable quality at competitive prices -...
-
Optimize Mold Machining with the Right Tools and Process Planning
Boost mold manufacturing productivity and tool life with the right machining strategies, tooling choices, and process planning.
-

How to Prevent Shrinkage in Die Castings
At present, the application of impregnation technology in the products of die-casting aluminum manufacturers is constantly expanding. China advocates for full i...

